This is where options hedging comes into play. Options provide a flexible way to minimize downside risk while maintaining upside potential. This guide will explain how options can be used as a hedge and introduce five essential hedging strategies every investor should know.
Why Use Options for Hedging?
Hedging with options allows investors to protect their portfolio against price declines while keeping their core investments intact. Unlike selling stocks outright (which can trigger taxes or remove exposure to future gains), options let investors maintain positions while offsetting potential losses.
Key Benefits of Hedging with Options
- Downside Protection: Reduce exposure to large losses without selling assets.
- Flexibility: Options allow partial or full hedging depending on risk tolerance.
- Cost Efficiency: Options are often cheaper than liquidating positions and repurchasing them later.
- Leverage: Small investments in options can provide substantial protection against losses.
1. Protective Puts: The Insurance Policy for Your Stocks
A protective put is one of the simplest and most effective ways to hedge a stock or portfolio. It functions like insurance, allowing investors to lock in a minimum selling price while maintaining upside potential.
How It Works
A protective put involves buying a put option for a stock or index you own. This gives you the right to sell the asset at a predetermined price (strike price), ensuring you don’t suffer excessive losses if the market drops.
Example: If you own 100 shares of XYZ stock at $100 per share, you can buy a put option with a strike price of $95 for a small premium. If XYZ falls to $80, your put option allows you to sell at $95, reducing losses.
Advantages and Considerations
Protective puts offer strong downside protection but come at a cost—the premium paid. The challenge is balancing the cost of protection against the likelihood of needing it. Investors typically use protective puts before earnings reports, economic releases, or periods of market uncertainty.
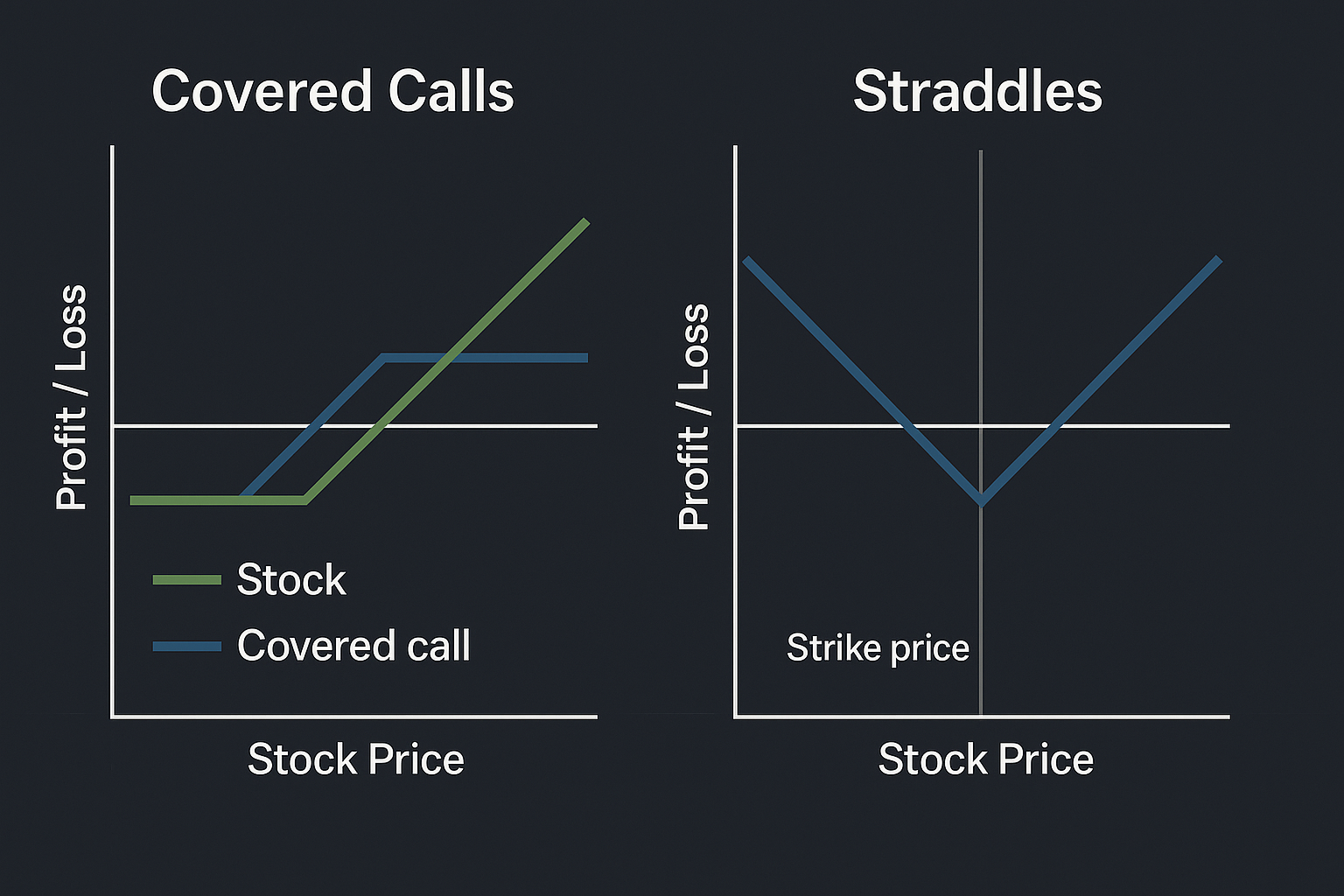
2. Covered Calls: Hedging While Generating Income
A covered call is a hedging strategy that also generates extra income. It involves selling a call option against stocks you own, collecting a premium while agreeing to sell the stock if it reaches the strike price.
How It Works
If you own 100 shares of ABC stock at $50, you can sell a call option with a strike price of $55 for $2 per share. If ABC stays below $55, you keep both your stock and the $200 premium (100 shares × $2). If ABC rises above $55, you must sell at that price but still keep the premium.
Advantages and Risks
Covered calls allow investors to earn extra income while holding their stocks, but they limit potential upside. If the stock price rises sharply beyond the strike price, you may miss out on larger gains. This strategy is best for investors who are neutral to moderately bullish on a stock.
3. Collars: Limiting Risk with Minimal Cost
A collar strategy combines a protective put and a covered call to hedge a stock position with minimal cost. It protects against significant losses without requiring a large premium payment.
How It Works
If you own 100 shares of XYZ at $100, you could:
- Buy a $95 put (protects against a drop below $95)
- Sell a $110 call (caps gains at $110 but reduces put costs)
By selling the call, the investor reduces the cost of the protective put, making it an affordable hedge. This strategy is especially useful during market uncertainty when an investor wants protection but also wants to avoid paying high option premiums.
When to Use a Collar Strategy
Collars are useful when investors want low-cost downside protection while maintaining long-term exposure to a stock. They are particularly effective when markets are volatile and options premiums are expensive.
4. Index Puts: Hedging a Portfolio Against Market Crashes
For investors holding diversified portfolios, buying index puts can provide broad market protection without needing to hedge each stock individually.
How It Works
Buying put options on major indices like the S&P 500 (SPX) or Nasdaq (NDX) allows investors to hedge against a general market decline. If the market falls, index puts increase in value, helping offset portfolio losses.
Example: If your portfolio closely follows the S&P 500, buying SPX put options allows you to hedge against a market downturn without selling individual stocks.
Best Use Cases
- During bear markets or recessions
- As a hedge against broad-based declines
- When holding a diversified portfolio but needing short-term protection
5. Ratio Put Spreads: Cost-Effective Downside Protection
A ratio put spread is a more advanced hedging strategy that provides limited downside protection at a reduced cost. It involves buying one put option and selling multiple lower-strike puts to offset the cost.
How It Works
If XYZ trades at $100, you could:
- Buy a $95 put
- Sell two $90 puts
This creates a hedge at a lower cost but does not fully protect against extreme declines. The risk increases if the stock falls far below the lower strike price.
Ideal Scenarios for Ratio Put Spreads
Ratio put spreads work best when traders expect minor declines rather than a full market crash. They help reduce hedging costs while still providing some downside protection.
Options Strategy Comparison
Conclusion
Hedging with options provides a strategic way to manage portfolio risk without liquidating investments. Strategies like protective puts, covered calls, collars, and index puts allow investors to protect against losses while maintaining long-term growth potential.
Each strategy has its own risk-reward tradeoffs, so choosing the right approach depends on market conditions, risk tolerance, and investment goals. For best results, investors should consider combining these techniques or adjusting their hedges based on market outlook.
Learn More
Want to learn more about hedging strategies?
Explore Tradesk’s educational resources for more insights into risk management and options trading.